The 5G is here: Qualcomm announces the 7 Gbps X55 modem and explains how it will change the Internet.
Qualcomm announced the new Snapdragon X55 modem, calling it the most advanced multi-mode model in the world: it can reach 7 Gbps on a 5G network and connect to 4G, 3G and 2G, representing a unique solution that is extremely effective and efficient.
The 5G is here. After years of anticipations and promises of a revolution based on the 4G LTE, the next-generation networks are finally close to debut. In reality, there are already but do not see, since there are no commercial products compatible with the new technology.
Users, businesses and municipalities cannot yet take advantage of the benefits in an extensive way, but now it’s just a matter of months: Qualcomm will introduce new commercial products based on 5G at Mobile World Congress 2019, and the business partners have them already in hand and have could implement them in the last few months within their projects.
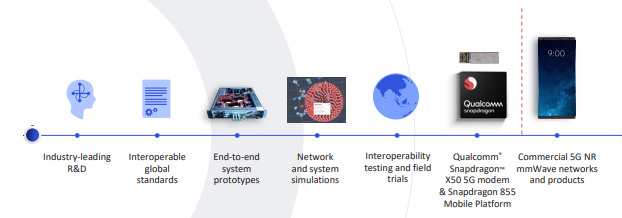
Let’s start with a few numbers: starting from 1985 the American company has invested about 55 billion dollars in research and development, and in recent years, a large part has been reserved for the development of solutions to simplify the implementation of technology in products of commercial partners.
At the same time, the 5G will be an indispensable technology to respond to the growth of data traffic expected for the next 5 years: according to the estimates of the Ericsson Mobility Report of November 2018, in 2024 data traffic will grow by 60 times compared to 2013 data and in absolute numbers? In 2024, the infrastructures will have to handle a traffic of 136 billion gigabytes per month of which a large part (75%) will be consumed with the creation or consumption of multimedia content.
In five years, 25% of global data traffic will be managed by a 5G network infrastructure. The new networks, in other words, will have to support 1.3 times the current traffic that occurs on all available network technologies, then 2G, 3G and 4G.
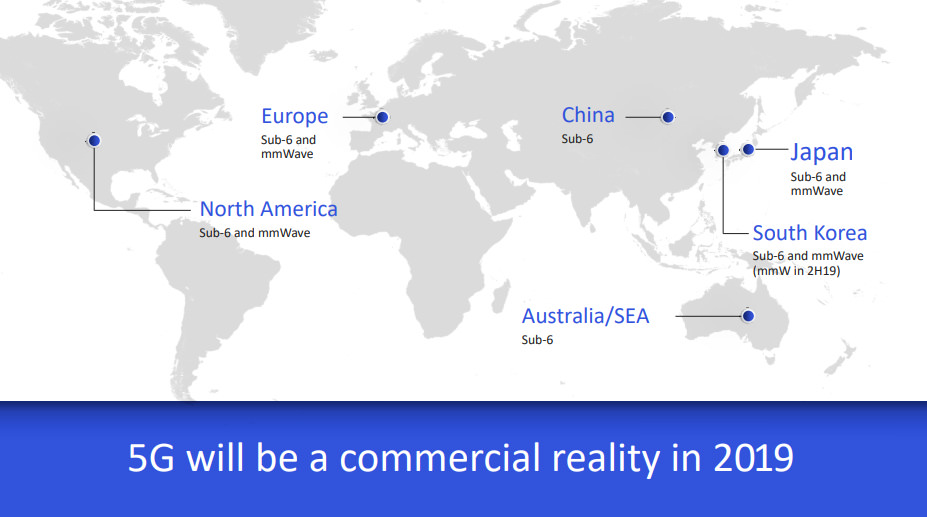
The revolution is set to begin in 2019: in the United States, Japan, South Korea and Europe, the Sub-6 and mmWave (millimeter-wave) technologies will arrive, while in China and Australia only the Sub-6 GHz will arrive. And here Qualcomm takes over: many of the commercial partners all over the world have already used the Snapdragon X50 modem to perform the first tests on technology, tests that mainly served to understand how to implement the whole on a commercial scale.
And the marketing of the first 5G networks will take place in 2019. The first launches are expected in TDD technology, but to extend the coverage in all areas of the world must also rely on the FDD. Initially, we will see connections in 5G with Sub-6 and mmWave frequencies (from 28 to 39 GHz), often exploiting combinations of frequencies not only between native 5G networks.
In the early days, it will be possible to connect to mixed 4G and 5G connections: the first commercial launches will exploit a Non-standalone infrastructure, so the device will first have to connect to a 4G network, and then it will start the connection in 5G when available. In the future, the Standalone networks will arrive, which will work in 5G without prior engagement in 4G.
The global launch will take place in the geographical areas indicated above and will immediately involve more than twenty device manufacturers worldwide and more than 20 global telephone operators.
Qualcomm Snapdragon X55, the second generation of 5G modem
In 2016, Qualcomm announced the first proprietary 5G modem, the Snapdragon X50, through which the first trials were conducted with third-party operators and companies. After about three years comes the new Qualcomm Snapdragon X55, the first 5G modem of the American company designed for a commercial debut, the first that we will see end users, but that will represent the second generation of Qualcomm 5G modem.
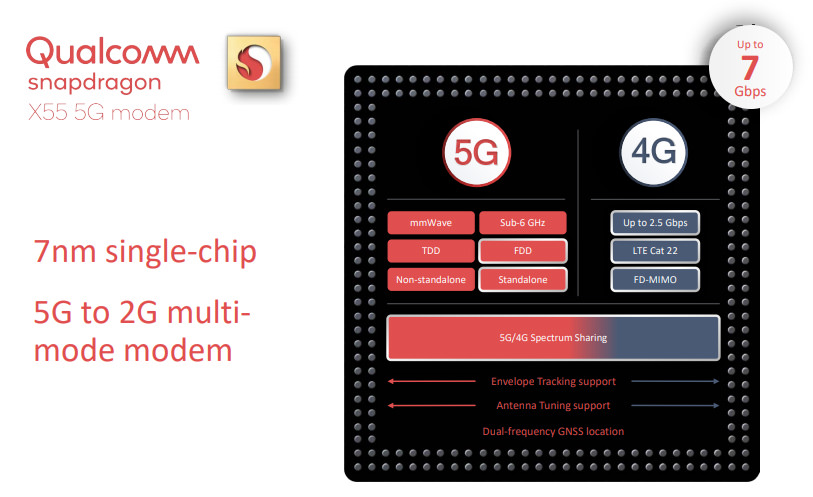
To adopt it will be several operators and OEM, for a total of over 30 products launched by the end of 2019. The Snapdragon X55 is a fully integrated modem, capable of supporting all existing network technologies starting from 2G up to the 5G.
A single modem to manage four different networks ensures great efficiency, but requires extensive architectural complexity. Above all because X55 wants to be complete also on the front of the support of the frequencies: Qualcomm has declared that its new modem is compatible with all combinations of frequency bands and works in all geographical areas in the world.
It will be present on smartphones, mobile hotspots, solutions for fixed wireless, notebooks, tablets, and even cars. It will support both non-standalone and standalone networks, and is ready not only for initial implementations, but also for subsequent ones.
Snapdragon X55 is made at 7-nm and can also use for the 5G connections the same frequencies adopted by 4G (4G / 5G Spectrum Sharing) whose licenses have already been paid by operators, and that could be exploited in some way for new networks.
The modem guarantees a download speed of 7 Gbps and 3 Gbps uploads over the 5G network, and supports LTE Cat. 22 for transfer speeds of 2.5 Gbps in download on the LTE network. It is compatible with both the Sub-6 GHz and the mmWave bands, supports the TDD and FDD modes and offers great transfer rates and full functionality all over the world on paper.
The new modem can be combined with a new antenna designed by Qualcomm and offer, virtually ready for use, to third-party companies. The goal is to make the 5G diffusion simpler and faster, allowing OEMs to introduce it on their devices as quickly as possible, and at reduced costs.
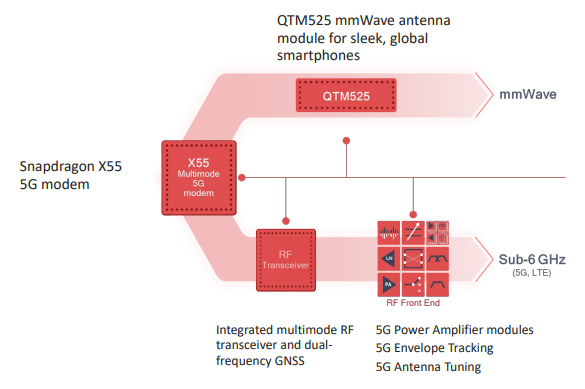
Qualcomm QTM525 mmWave Antenna Module is designed for smartphones even less than 8 mm thick, supports the bands 26 GHz, 28 GHz and 39 GHz and has been realized paying great attention to the size so you can be inserted into devices from the form factor increasingly aggressive.
Qualcomm is already able to offer OEMs a complete platform for the implementation of 5G on products from the most disparate categories, thus reducing production costs and timing for placing on the market.
The company offers an integrated solution equipped with a QTM525 antenna, a Snapdragon X55 modem, Power Amplifier 5G modules, and systems for Envelope Tracking and for the Tuning Antenna. Through the platform, the OEM cannot only implement the 5G quickly within its own devices, but can do it immediately in an efficient and reliable way.
We talked about 5G Envelope Tracking, which we explain briefly. With the technology, the signal released by the phone can be modulated both in frequency and in amplitude: to reach the peak needed at a given time the signal needs a particular voltage, and without Envelope Tracking or dynamic adaptation would waste power.
With the technology, it is possible to detect the waveform in real time and reduce the power to the minimum value to emit a signal with the right width, without wasting the band. This allows up to twice the energy efficiency, higher speed, and greater autonomy for the devices, as well as a superior indoor coverage.
The advantages of 5G, some practical examples
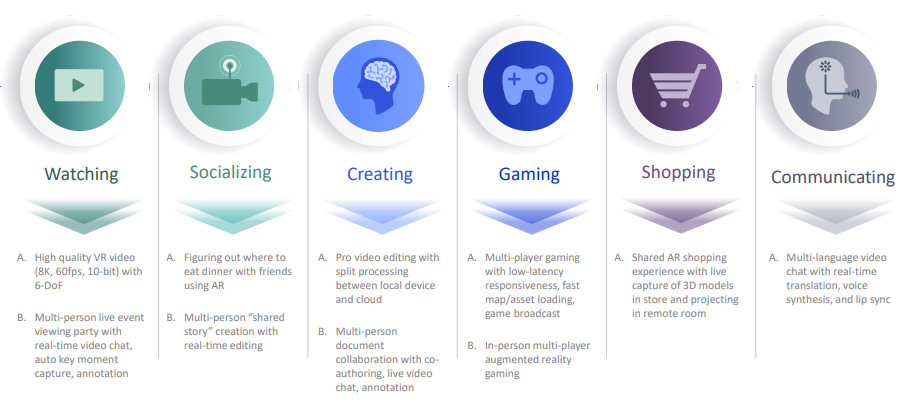
But what is the use of 5G and do we really feel the need? It seems that the 4G has effectively covered the needs of the vast majority of users: the speed of transfer is often overflowing and the latencies are also satisfying for online gaming. Qualcomm explains that the 5G will give the possibility to perform operations that today are simply impossible with the current mobile network technologies. Here are some:
High-quality video VR
With the new networks, it will be possible to manage real-time and high-quality experiences of high-quality virtual reality with volumetric audio and video. Those who live the experience can navigate in the three-dimensional environment, walking inside it and seeing the effects inside the simulation.
See multi-stream video and audio
The new networks will allow you to view events (such as sporting events, concerts, and much more) from multiple angles, even simultaneously. An Artificial Intelligence system can identify key moments by proposing them in the main a box, or the faces of friends and participants can be played with the automatic capture of their reactions.
Augmented reality for the discovery of local or places to visit
On the screen of the smartphone could appear an overlay with names, reviews and scores of local and places to visit, with the ability to share everything with friends to organize the meeting.
Creation of stories in a collaborative way
The 5G will also allow to enable collaborative editing features even on large projects. Each member can insert his own piece of shared history, which is made up of audio-video elements from multiple sources.
Professional video editing with much smaller and lighter devices
The collaboration possibilities will not be open only to the consumer user, but thanks to the speed and latencies of the networks even professionals can take advantage of it. For example: heavy operations can be carried out even with small and light devices, small batteries and low-powered hardware. In the case of video, editing all the processing would take place on remote servers with the project saved in the cloud. The final result will then be processed in real time by remote servers, and sent in streaming on-demand at full quality.
Gaming
In gaming, 5G will offer lower latency than today’s mobile network technologies. In addition, the maps and game environments could be loaded instantly because saved remotely without taking up space on the smartphone or the device in general.
Players could send gameplay to friends or fans in real time, while multi-language voice conversations could take place with real-time translations through natural language processing and speech synthesis technologies. The 5G could enable the ability to play in augmented reality, or exploiting the real environment as a game environment.
Multi-language videoChat
one of the most interesting features of 5G will be the possibility of exploiting various technologies together to make life easier for users. An example can be a video chat between two people who speak different languages, with user A speaking language A and user B speaking language B.
A depth camera can analyze the face of A and three neural networks in three dimensions different can elaborate: natural language, translating it into a language B; the vocal synthesis transforming the voice of A so that it expresses the words in the language B; and finally the last neural network can modify in three dimensions the face of A synchronizing the lips with the words of the language B. As a result, the user B would see an avatar of A as if speaking in the language B moving consequently, the lips in sync with the language B.
At Mobile World Congress 2019, Qualcomm will show some demos of the experiences we have described above. Naturally, the company will stop at the previous step and will not release these experiences. Its goal is indeed to offer business partners a basis on which to plan the future of the world of networks and technology in a broader sense.